Sanctioned Chinese National Still Active on US Tech Platforms
Despite facing U.S. sanctions for his alleged role in facilitating virtual currency investment scams, Chinese national Liu “Steve” Lizhi, also known as XXL4, continues to maintain a presence on several major American tech platforms, including GitHub, Facebook, and X. This raises questions about the effectiveness of sanctions enforcement by these companies.
Funnull Technology and “Pig Butchering” Scams
In May 2025, the U.S. Department of the Treasury announced sanctions against Funnull Technology Inc., a Philippines-based company, and its alleged operator, Liu Lizhi. Funnull is accused of providing infrastructure for hundreds of thousands of websites involved in “pig butchering” scams,which have resulted in over $200 million in losses for Americans. These scams involve building trust with victims before defrauding them of their money through cryptocurrency investments.
Funnull reportedly operated as a content delivery network catering to cybercriminals seeking to route traffic through U.S.-based cloud providers. The Treasury Department stated that Funnull’s operations where linked to the majority of pig butchering scams reported to the FBI.
Did You Know? Pig butchering scams are named for the practice of “fattening up” victims with attention and false promises before defrauding them.
Lizhi’s Continued Presence on Tech Platforms
Despite the sanctions, Lizhi has maintained active accounts on various tech platforms. A GitHub profile associated with Lizhi, using the nickname XXL4, hosts an open-source e-commerce platform called Nexamerchant, which claims to work with numerous American financial institutions. While GitHub has a process for identifying sanctioned users, it locks accounts rather of removing them, allowing access to public repositories.
Liu Lizhi also operates numerous Facebook accounts and groups, including one for an entity specified in the OFAC sanctions: The “Enjoy Ganzhou” tourism page for Ganzhou, China.
Meta confirmed it has closed the accounts and groups connected to Mr. Lizhi.
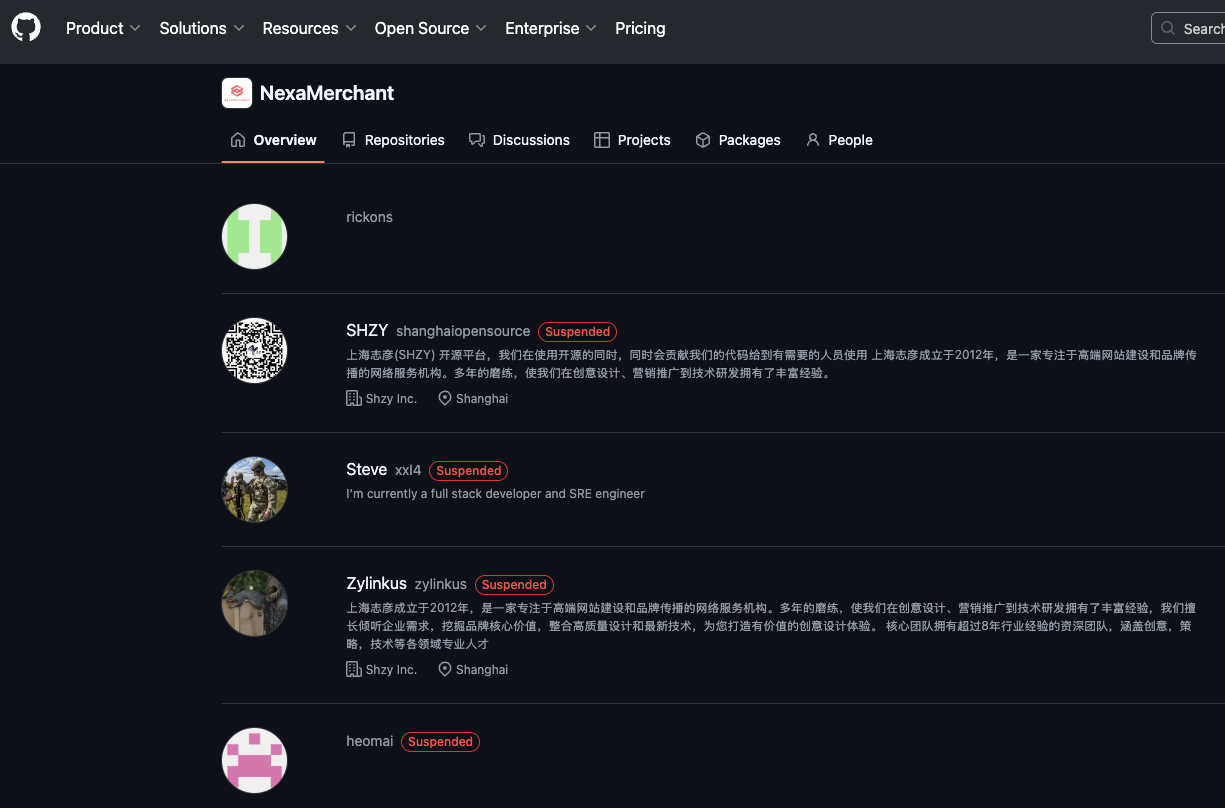
All of the follower accounts for the XXL4 GitHub account appear to be Mr. lizhi’s, and have been suspended by GitHub, but their code is still accessible.
The Role of Tech Companies in Enforcing Sanctions
The situation highlights the challenges tech companies face in enforcing U.S. sanctions. While financial institutions have mature systems for identifying and severing ties with sanctioned individuals, tech companies might potentially be less proactive, especially with free accounts. This discrepancy poses a potential risk and liability for tech companies, depending on the extent to which the Office of Foreign Assets control (OFAC) is willing to enforce regulations.
According to a 2023 report by Kharon, financial institutions are increasingly leveraging advanced technologies like AI and machine learning to enhance their sanctions screening processes, improving accuracy and efficiency Kharon.
funnull’s Evolving Tactics
Following the sanctions, Funnull appears to be adapting its tactics to evade detection. This includes using a larger number of domain generation algorithms (DGAs) to create numerous similar but unique website names, making their infrastructure more arduous to track.
Pro Tip: Organizations should proactively monitor for and block domains associated with known malicious actors to mitigate the risk of falling victim to their schemes.
Timeline of Events
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| November 13, 1984 | Liu “Steve” Lizhi’s birth date. |
| July 2024 | Funnull purchased the domain polyfill[.]io, later used in a supply-chain attack. |
| May 2025 | U.S.Treasury Department announces sanctions against Funnull Technology Inc. and Liu Lizhi. |
What measures should tech companies take to ensure compliance with U.S. sanctions? How can international cooperation be improved to combat cybercrime and financial fraud?
Evergreen Insights: The broader Context of Sanctions and Cybercrime
the case of Liu Lizhi and funnull Technology highlights the ongoing challenge of combating cybercrime and enforcing international sanctions in the digital age. Cybercriminals are increasingly sophisticated, using advanced techniques to evade detection and exploit vulnerabilities in online platforms. The global nature of the internet makes it difficult to track and prosecute these actors, requiring international cooperation and innovative solutions.
Sanctions are a powerful tool for disrupting illicit activities,but their effectiveness depends on robust enforcement by both governments and private companies. tech platforms play a crucial role in this process, as they provide the infrastructure and services that cybercriminals rely on. by implementing strong compliance measures and working with law enforcement agencies, tech companies can help to prevent their platforms from being used for illegal purposes.
Frequently Asked questions About U.S. Sanctions and Cybercrime
- What are U.S. sanctions, and how do they work?
- U.S.sanctions are economic and trade restrictions imposed by the U.S. government against individuals, entities, and countries that are deemed to be a threat to national security, foreign policy, or economic stability. These sanctions can include asset freezes, travel bans, and restrictions on trade and financial transactions.
- Why was Funnull Technology sanctioned by the U.S.government?
- Funnull Technology was sanctioned for allegedly providing infrastructure for websites involved in virtual currency investment scams, also known as “pig butchering” scams, which resulted in significant financial losses for Americans.
- How do “pig butchering” scams work?
- “Pig butchering” scams involve building trust with victims over time, often through online dating or social media, before defrauding them of their money through cryptocurrency investments. The scammers “fatten up” their victims with attention and false promises before “butchering” them by stealing their money.
- What are the responsibilities of tech companies in enforcing U.S. sanctions?
- Tech companies are expected to comply with U.S. sanctions by implementing measures to prevent sanctioned individuals and entities from using their platforms for illegal activities. This can include screening users, blocking access to services, and reporting suspicious activity to law enforcement agencies.
- what are domain generation algorithms (DGAs), and how are they used by cybercriminals?
- Domain generation algorithms (DGAs) are programs that generate large numbers of similar but unique domain names for websites. Cybercriminals use DGAs to create websites that are difficult to track and block,as they can quickly switch to different domain names and IP addresses when legitimate providers attempt to take the websites down.
- What steps can individuals take to protect themselves from virtual currency investment scams?
- Individuals can protect themselves by being wary of unsolicited investment offers, especially those that promise high returns with little risk. It is also crucial to do thorough research before investing in any cryptocurrency and to be cautious of individuals who pressure you to invest quickly.
Share your thoughts in the comments below and help us spread awareness about the importance of cybersecurity!

