The Mayan Collapse: Droughts revealed as a Key Factor
Table of Contents
Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico – A groundbreaking study reveals that a series of severe droughts, spanning over 150 years, likely played a pivotal role in the decline of the Mayan civilization. Scientists analyzing mineral deposits within a cave system on the Yucatán Peninsula have reconstructed a detailed climate record, pinpointing multiple periods of prolonged dryness between 871 and 1021 AD.This research offers compelling evidence supporting the theory that climate change significantly impacted the onc-thriving mesoamerican society.
Unearthing the Past Through Cave Formations
The research team focused on stalagmites – cave formations created by mineral-rich water dripping over centuries. Like tree rings, the layers within stalagmites preserve a record of annual rainfall. By analyzing the oxygen isotopes in these layers, scientists were able to reconstruct the region’s wet and dry seasons with unprecedented precision. This method allows for a granular understanding of past climate conditions, far exceeding the resolution of previous studies based on lake sediments.
“Lacustrine sediments provide a broad overview, but stalagmites allow us to access the finer details that were previously lost,” explained the researchers. This detailed record revealed a catastrophic drought lasting 13 years, alongside seven other extended dry periods of at least three years each.
Did You Know? The Maya developed sophisticated water management systems, including reservoirs and underground cisterns, to cope with seasonal variations in rainfall. However, these systems were ultimately insufficient to withstand the prolonged and severe droughts identified in the study.
A Civilization Under Pressure
The mayan civilization, at its height, was a densely populated and culturally advanced society. Interaction and cultural exchange with other Mesoamerican civilizations, such as the Aztec and Olmec, contributed to its dynamism. However, the prolonged droughts placed immense strain on Mayan society, impacting agricultural production and threatening the survival of its large urban centers.
The study, published in Science Advances, points to a correlation between the drought periods and a cessation of monument building with dated inscriptions – a hallmark of Mayan culture. This suggests that resources and attention shifted from monumental construction to securing basic survival needs. The Maya civilization began a northward migration, ultimately contributing to its decline.
| Drought period | Duration (Years) |
|---|---|
| Catastrophic Drought | 13 |
| Prolonged Dry periods (x7) | ≥ 3 |
| Study Timeframe | 871 – 1021 AD |
The Role of Climate Stress
While theories abound regarding the Mayan collapse – including warfare, trade disruptions, and political instability – the new research underscores the critical role of climate stress. Daniel H. James, the lead author of the study, noted, ”Multiple theories have emerged about the cause of collapse… But in recent decades, we have begun to learn a lot about what happened to the Maya and why, combining archaeological data with quantifiable climatic evidence.”
The Maya’s ingenious hydraulic systems, while effective for managing seasonal fluctuations, proved inadequate in the face of multi-year droughts. Prolonged water scarcity jeopardized agricultural yields and threatened the sustainability of densely populated cities. What other factors, beyond climate, might have exacerbated the challenges faced by the Maya?
Pro Tip: Understanding past climate events can provide valuable insights into the potential impacts of modern climate change on vulnerable populations and ecosystems.
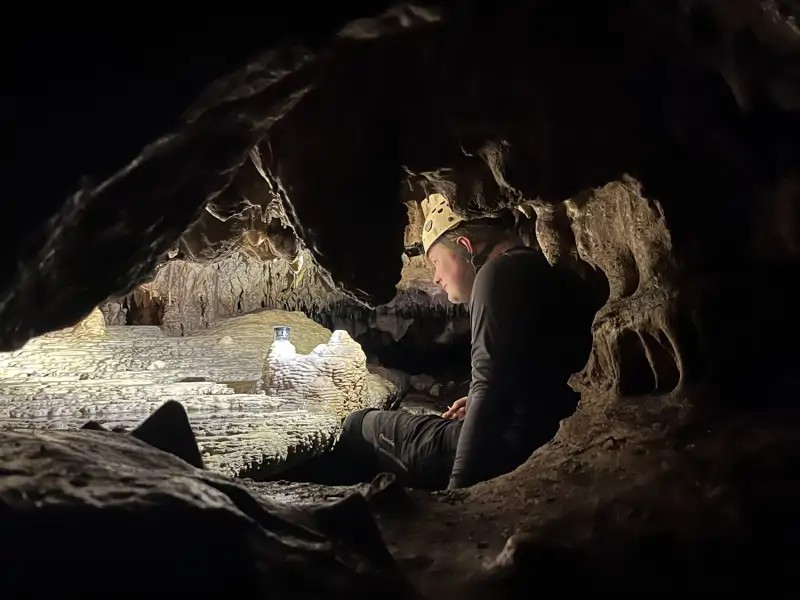

researcher Daniel H. James installs a drip monitor in las Grutas Tzabnah (yucatán,Mexico) as part of the ongoing monitoring campaign.
sebastian Breitenbach
Researchers plan to expand the network of cave monitoring sites to create a more comprehensive climatic chronology and further refine our understanding of the interplay between climate,Mayan decision-making,and the civilization’s ultimate decline.
The collapse of the Mayan civilization serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of even the most advanced societies to environmental change.While the specific factors contributing to the Mayan decline were complex and multifaceted, the role of prolonged drought is increasingly recognized as a critical component. This historical case study offers valuable lessons for contemporary societies facing the challenges of climate change and resource management. Ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of the Mayan past, providing insights into the resilience and adaptability of human civilizations.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Mayan Collapse
- What was the primary cause of the Mayan collapse? While multiple factors contributed, recent research strongly suggests prolonged droughts played a significant role.
- how did scientists determine the extent of the droughts? By analyzing oxygen isotopes in stalagmites found in caves on the Yucatán Peninsula.
- What impact did the droughts have on Mayan society? They led to agricultural failures, resource scarcity, and ultimately, the decline of major Mayan cities.
- Were there other factors contributing to the Mayan decline? Yes, theories include warfare, trade disruptions, and political instability.
- What can we learn from the Mayan collapse? It highlights the vulnerability of civilizations to climate change and the importance of sustainable resource management.
This research offers a compelling glimpse into the past, reminding us of the delicate balance between civilization and the environment. We invite you to share this article with your network, leave a comment with your thoughts, and subscribe to our newsletter for more in-depth coverage of historical discoveries and their relevance to our world today.