Geophysics Explores Earth’s Hydrogen Potential
Uncovering Natural Hydrogen Sources for Clean Energy
The quest for sustainable energy sources has led scientists to explore an unlikely frontier: natural hydrogen. This element, when burned, yields only heat and water, offering a promising alternative to fossil fuels. Recent research has focused on how this “white gold” might be produced naturally by the earth itself.
Natural Hydrogen Formation in Rocks
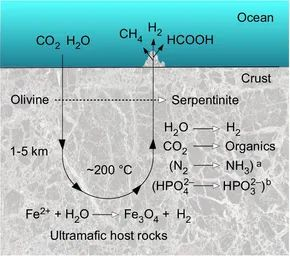
Geoscientists have discovered that hydrogen can occur naturally within rocks. This process, known as serpentinization, involves ultramafic rocks interacting with water under low pressure and temperature. It produces serpentine minerals and hydrogen gas, which gets trapped within the rocks.
The ultramafic rocks, or ophiolites, are remnants of the oceanic crust pushed to the surface through tectonic processes. During serpentinization, water enters the crust, reacting with ultramafic rocks. Iron in olivine is oxidized by water, producing iron oxide and hydrogen. This reduction process converts water into hydrogen gas, along with other compounds.
Geological Hydrogen in Indonesia
Central Sulawesi, Indonesia, has a large concentration of ultramafic rocks. In October 2023, the Geological Agency researched the One Pute Jaya area in Morowali Regency, Central Sulawesi, to assess natural hydrogen potential. Their study discovered a hot spring that contained hydrogen gas. This gas emerged from the serpentinization process, with the Matano fault possibly acting as a migration pathway.
Geophysics and Hydrogen Exploration
Serpentinization alters rock formations’ magnetic and physical properties. The creation of magnetite minerals increases magnetic susceptibility. Increased magnetization may signal the process’s occurrence. Additionally, density decreases because serpentinization creates fractures and pores. The seismic experiment revealed that lower seismic speeds can be attributed to serpentinization, reflecting a lower density. Furthermore, fresh peridotite is more electrically resistive than serpentinized peridotite, which is attributable to higher porosity. This conductive response helps in locating cracked or saturated serpentinite crust. These changes help geophysicists explore ultramafic rocks with the potential to produce natural hydrogen to satisfy future energy demands.
The global hydrogen market is projected to reach $130 billion by 2030, driven by increasing demand across various sectors (Grand View Research 2024).
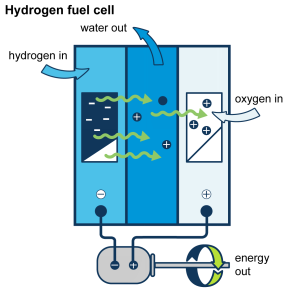
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cells represent a promising technology for converting hydrogen energy into electricity. Within these cells, hydrogen and oxygen combine, producing water and generating electricity. This process could be a suitable substitute for fuel oil, offering a pathway towards cleaner energy production.
The study of natural hydrogen and its extraction is critical for sustainable energy. The ability to produce clean energy without harmful emissions makes hydrogen a viable solution for environmental protection and a sustainable future.

