Human Embryo Implantation Captured in Stunning Time-Lapse
Table of Contents
Barcelona, Spain - In a scientific first, researchers have successfully captured the dynamic process of human embryo implantation using advanced time-lapse microscopy. The groundbreaking footage offers unprecedented insight into the earliest stages of human development, possibly revolutionizing our understanding of infertility and early pregnancy loss.
The Challenge of Studying Implantation
For decades, the intricacies of human embryo implantation-when a developing embryo attaches to the uterine lining-have remained largely hidden from view. “It’s very inaccessible because it’s all happening inside the mother,” explained Samuel ojosnegros, a bioengineer at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in Barcelona, Spain.This critical process, essential for establishing a viable pregnancy, has proven difficult to study directly due to its location and complexity.
A Novel Approach: Synthetic Uterine Lining
To overcome these challenges, the IBEC team devised a sophisticated method using a synthetic uterine lining. Unlike previous attempts using glass surfaces, this innovative model was constructed from a gel rich in collagen and proteins vital for embryonic development, mimicking the natural surroundings more accurately. This allowed researchers to observe the embryo’s interaction wiht a more realistic substrate.
Researchers utilized donated human embryos and captured images approximately every 20 minutes over a 16- to 24-hour period. These images were then compiled into a time-lapse film, revealing the embryo actively pulling on and embedding itself within the gel. This process demonstrates the embryo’s ability to remodel its environment,a crucial step in prosperous implantation.
Did You No? Mouse embryos, unlike their human counterparts, tend to adhere to the uterine surface rather than actively embedding themselves within it, highlighting key species-specific differences in implantation.
Key Findings and Visual Evidence
The resulting footage revealed that human embryos actively contract themselves to minimize exposure to the external environment. Furthermore, the embryos were observed applying force to pull apart the synthetic tissue, demonstrating a proactive role in establishing implantation. Amélie Godeau, a biomechanics researcher at IBEC, noted her initial surprise at the speed with which the embryos burrowed into the gel, initially suspecting an experimental error.
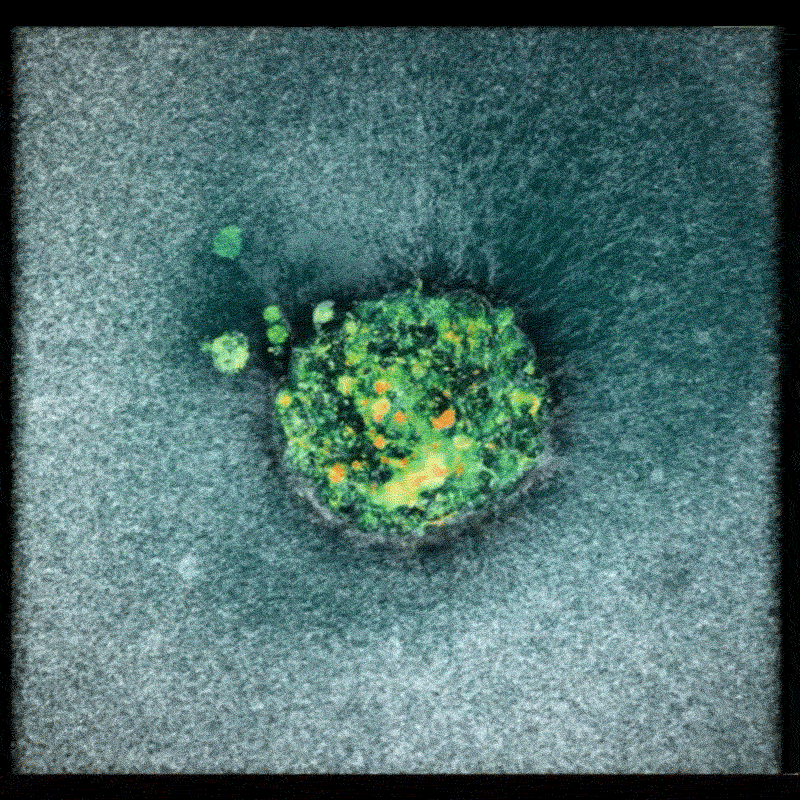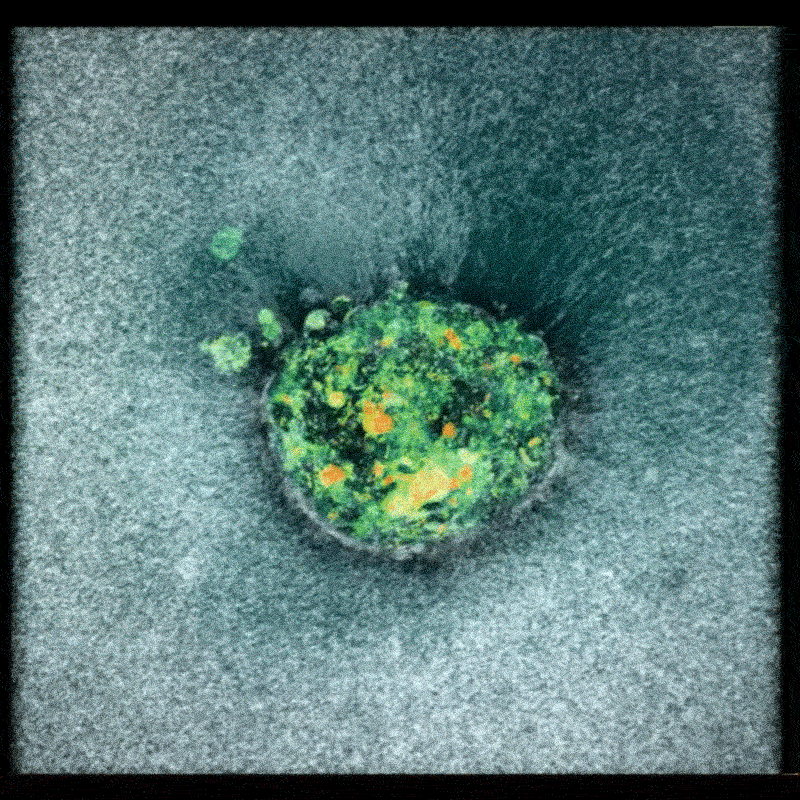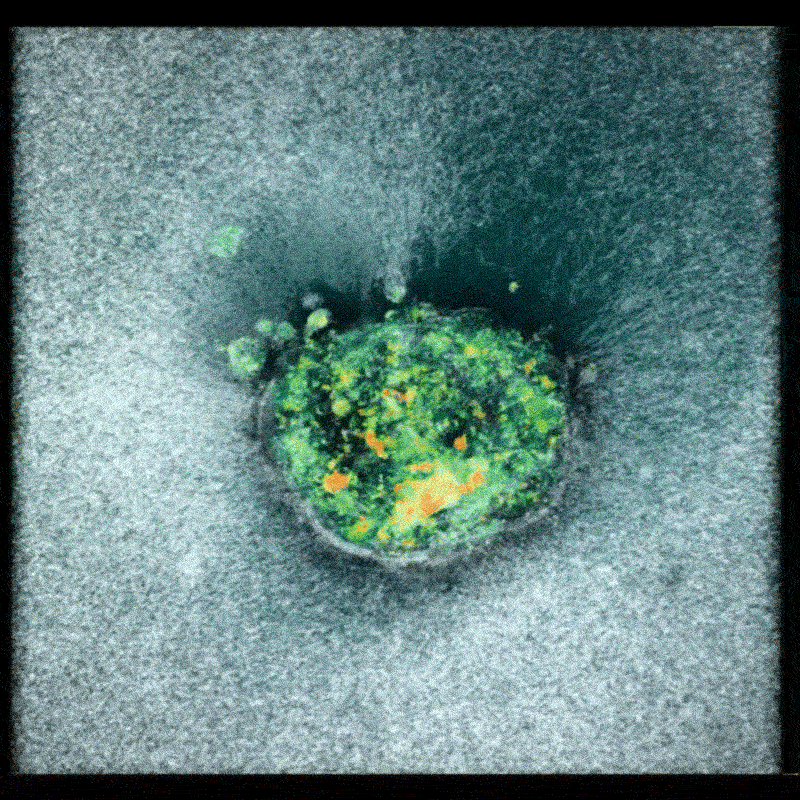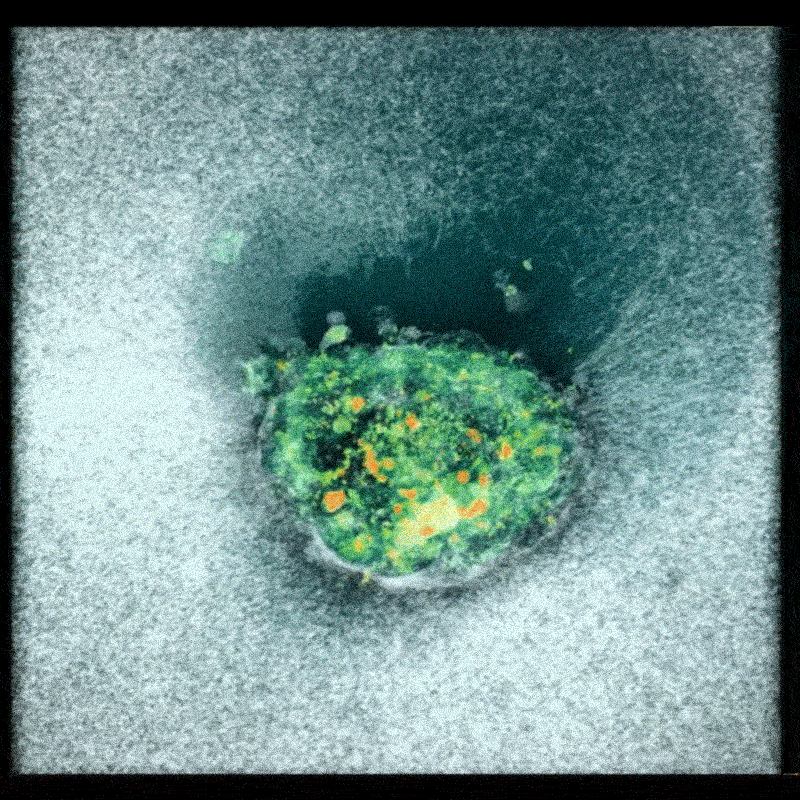
Implications for Reproductive Health
This research, published today in Science Advances1, has meaningful implications for understanding and addressing infertility. by visualizing the implantation process,scientists can gain valuable insights into the factors that contribute to implantation failure,a common cause of early pregnancy loss. What role do uterine receptivity markers play in this process, and how can we better assess them?
Pro Tip: Understanding the mechanics of implantation coudl lead to the development of new diagnostic tools and therapies to improve success rates for in vitro fertilization (IVF) and other assisted reproductive technologies.
Key Data Summary
| metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Institution | institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), Barcelona, Spain |
| Publication Date | August 16, 2025 |
| Journal | Science Advances |
| Imaging Frequency | Approximately every 20 minutes |
| Duration of Observation | 16-24 hours |
The team’s work builds upon decades of research into the complexities of early human development. Previous studies have explored embryo-surface interactions, but the use of a more physiologically relevant synthetic lining represents a significant advancement. This allows for a more accurate depiction of the forces and mechanisms involved in successful implantation. Could this technology eventually lead to the creation of fully functional artificial wombs?
The study of human implantation remains a critical area of research, with ongoing efforts to unravel the molecular and cellular mechanisms that govern this process. Advances in bioengineering and imaging technologies are continually pushing the boundaries of what is possible, offering hope for improved reproductive outcomes for millions of individuals worldwide. Future research will likely focus on refining the synthetic uterine lining to more closely mimic the natural environment and investigating the role of genetic factors in implantation success.
Frequently Asked Questions about Human Embryo Implantation
- What is human embryo implantation? It’s the process where a developing embryo attaches to the uterine lining, essential for establishing a pregnancy.
- Why is studying implantation so difficult? The process occurs inside the mother’s body, making direct observation challenging.
- What is a synthetic uterine lining? It’s a lab-created gel that mimics the natural environment of the uterus, allowing researchers to study embryo interactions.
- How does this research help with infertility? By understanding implantation, scientists can develop better diagnostic tools and therapies for infertility.
- What were the key findings of this study? Researchers observed human embryos actively pulling on and embedding themselves within the synthetic uterine lining.
This research offers a compelling glimpse into a fundamental process of human life. We invite you to share this article with your network and join the conversation about the future of reproductive health. Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest breakthroughs in science and medicine.

