South Korea’s Myopia Epidemic: Echoes of China‘s ’Child Myopia’ Concerns
Table of Contents
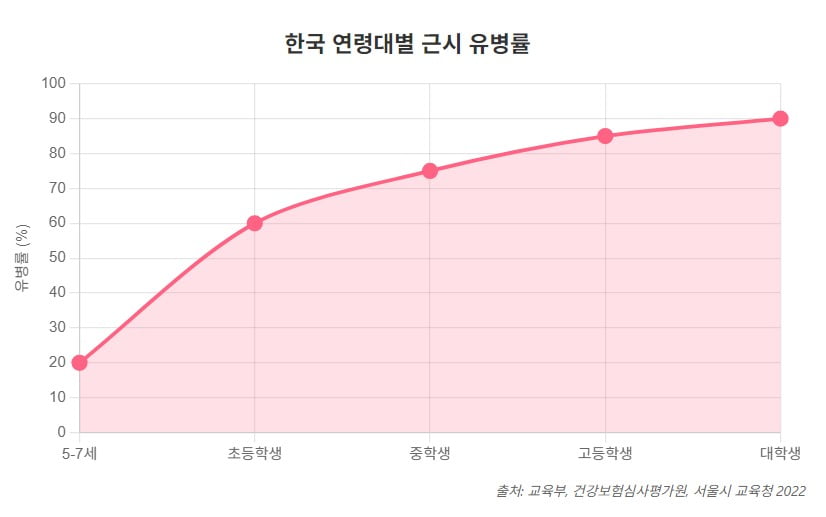
Seoul – South Korea is grappling with an unprecedented surge in myopia, particularly among young people, raising concerns about long-term economic and societal impacts. The situation is drawing parallels to recent anxieties in China regarding childhood nearsightedness, prompting questions about the role of educational policies and lifestyle factors. The number of visits related to myopia reached 284,532 in 2019, the highest across all age groups, representing 36% of all patient visits, according to the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. Experts predict the rate has likely worsened since then.
The prevalence of myopia in South Korea has transformed the nation into what some are calling a “national glasses era,” creating a ample market for vision correction. The domestic eyeglass lens market is estimated at approximately 600 billion won (approximately $460 million USD as of September 8, 2025) this year. The Ahn Kwang-hak equipment market – encompassing diagnostic and treatment tools – is projected to expand from $12.5 billion to $17.6 billion by 2030.When factoring in ophthalmology, cataract surgery, and refractive surgery, Korea’s overall “vision economy” is estimated to be worth 3 to 4 trillion won (approximately $2.3 to $3.1 billion USD) annually.
The escalating myopia rates are prompting scrutiny of factors similar to those under discussion in China, where policies promoting intense academic study have been linked to a rise in childhood nearsightedness. the pressure to succeed academically is immense in both countries, and that pressure is taking a toll on the eyesight of our children,
noted a recent report by the Korean Ophthalmological Society.
Key Statistics: South Korea’s Myopia Crisis
| Metric | Value (2019) | Projected (2030) |
|---|---|---|
| Myopia Visits | 284,532 | N/A |
| % of Total Visits | 36% | N/A |
| Eyeglass Lens Market | 600 Billion Won | N/A |
| Ahn Kwang-hak Market | $12.5 Billion | $17.6 Billion |
| Vision Economy | 3-4 Trillion Won | N/A |
Did You Know?
South Korea has one of the highest rates of myopia in the world, with estimates suggesting that over 90% of young adults are affected.
Pro Tip:
Regular eye exams are crucial for early detection and management of myopia.Encourage children to spend time outdoors and limit prolonged screen time.

The situation is prompting debate about potential policy interventions, mirroring discussions in China regarding reducing academic workloads and promoting healthier lifestyles for children. The long-term consequences of widespread myopia extend beyond individual health, perhaps impacting military readiness – as the saying goes, You can’t join the army without glasses
– and the overall productivity of the workforce.
what steps can South Korea take to address this growing public health concern? And how will the nation balance academic achievement with the well-being of its youth?
By Kim Joo-wan, reporter kjwan@hankyung.com
Myopia, or nearsightedness, is a refractive error where distant objects appear blurry. While genetics play a role, environmental factors – particularly near work and limited outdoor time – are increasingly recognized as significant contributors. The global prevalence of myopia has been rising rapidly in recent decades, particularly in East Asia. This trend is linked to increased urbanization, higher levels of education, and changes in lifestyle. Early intervention, such as specialized contact lenses or eye drops, can help slow the progression of myopia in children.
Frequently Asked Questions About Myopia in South Korea
- What is causing the rise in myopia in South Korea? The increase is attributed to a combination of factors,including intense academic pressure,prolonged near work (studying,screen time),and limited time spent outdoors.
- How does myopia impact the South Korean economy? The high prevalence of myopia drives significant spending on eyeglasses, contact lenses, and vision correction procedures, creating a multi-billion dollar “vision economy.”
- Is the situation in South Korea similar to China’s myopia crisis? Yes, both countries face high rates of childhood myopia, and both are examining the role of educational policies and lifestyle factors.
- What can be done to prevent or slow down myopia progression? Encouraging outdoor time, reducing near work, and regular eye exams are crucial. Specialized treatments like orthokeratology (ortho-k) and atropine eye drops may also be recommended.
- What are the long-term health risks associated with high myopia? High myopia increases the risk of developing serious eye conditions such as retinal detachment, glaucoma, and macular degeneration.
If you found this article informative,please share it with your network and join the conversation in the comments below. We’d love to hear your thoughts on this important issue!

